Trading characteristics
Most traded currencies[2]
Currency distribution of reported FX market turnover | Rank | Currency | ISO 4217 code
(Symbol) | % daily share
(April 2007) |
| 1 |  United States dollar United States dollar | USD ($) | 86.3% |
| 2 |  Euro Euro | EUR (€) | 37.0% |
| 3 |  Japanese yen Japanese yen | JPY (¥) | 17.0% |
| 4 |  Pound sterling Pound sterling | GBP (£) | 15.0% |
| 5 |  Swiss franc Swiss franc | CHF (Fr) | 6.8% |
| 6 |  Australian dollar Australian dollar | AUD ($) | 6.7% |
| 7 |  Canadian dollar Canadian dollar | CAD ($) | 4.2% |
| 8-9 |  Swedish krona Swedish krona | SEK (kr) | 2.8% |
| 8-9 |  Hong Kong dollar Hong Kong dollar | HKD ($) | 2.8% |
| 10 |  Norwegian krone Norwegian krone | NOK (kr) | 2.2% |
| 11 |  New Zealand dollar New Zealand dollar | NZD ($) | 1.9% |
| 12 |  Mexican peso Mexican peso | MXN ($) | 1.3% |
| 13 |  Singapore dollar Singapore dollar | SGD ($) | 1.2% |
| 14 |  South Korean won South Korean won | KRW (₩) | 1.1% |
| Other | 14.5% |
| Total | 200% |
There is no unified or centrally cleared market for the majority of FX trades, and there is very little cross-border regulation. Due to the over-the-counter (OTC) nature of currency markets, there are rather a number of interconnected marketplaces, where different currencies instruments are traded. This implies that there is not a single exchange rate but rather a number of different rates (prices), depending on what bank or market maker is trading, and where it is. In practice the rates are often very close, otherwise they could be exploited by arbitrageurs instantaneously. Due to London's dominance in the market, a particular currency's quoted price is usually the London market price. A joint venture of the Chicago Mercantile Exchange and Reuters, called Fxmarketspace opened in 2007 and aspired but failed to the role of a central market clearing mechanism.
The main trading center is London, but New York, Tokyo, Hong Kong and Singapore are all important centers as well. Banks throughout the world participate. Currency trading happens continuously throughout the day; as the Asian trading session ends, the European session begins, followed by the North American session and then back to the Asian session, excluding weekends.
Fluctuations in exchange rates are usually caused by actual monetary flows as well as by expectations of changes in monetary flows caused by changes in gross domestic product (GDP) growth, inflation (purchasing power parity theory), interest rates (interest rate parity, Domestic Fisher effect, International Fisher effect), budget and trade deficits or surpluses, large cross-border M&A deals and other macroeconomic conditions. Major news is released publicly, often on scheduled dates, so many people have access to the same news at the same time. However, the large banks have an important advantage; they can see their customers' order flow.
Currencies are traded against one another. Each pair of currencies thus constitutes an individual product and is traditionally noted XXXYYY or YYY/XXX, where YYY is the ISO 4217 international three-letter code of the currency into which the price of one unit of XXX is expressed (called base currency). For instance, EURUSD or USD/EUR is the price of the euro expressed in US dollars, as in 1 euro = 1.5465 dollar. Out of convention, the first currency in the pair, the "base" currency, was the stronger currency at the creation of the pair. The second currency, counter currency or "term" currency, was the weaker currency at the creation of the pair. Currencies are occasionally incorrectly quoted with the pairs inverted e.g. EUR/USD but this is incorrect. The "/" acts the same as the divide mathematical operator and derives the actual exchange rate. e.g. an amount of $140,000 equates to €100,000. $140,000/€100,000 = $/€ = USD/EUR = a rate of 1.4 hence EURUSD or USD/EUR. See Exchange_rate
The factors affecting XXX will affect both XXXYYY and XXXZZZ. This causes positive currency correlation between XXXYYY and XXXZZZ.
On the spot market, according to the BIS study, the most heavily traded products were:
-
- EURUSD: 27%
- USDJPY: 13%
- GBPUSD (also called cable): 12%
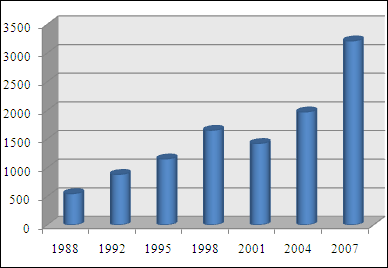
and the US currency was involved in 86.3% of transactions, followed by the euro (37.0%), the yen (17.0%), and sterling (15.0%) (see table). Volume percentages for all individual currencies should add up to 200%, as each transaction involves two currencies.
Trading in the euro has grown considerably since the currency's creation in January 1999, and how long the foreign exchange market will remain dollar-centered is open to debate. Until recently, trading the euro versus a non-European currency ZZZ would have usually involved two trades: EURUSD and USDZZZ. The exception to this is EURJPY, which is an established traded currency pair in the interbank spot market. As the dollar's value has eroded during 2008, interest in using the euro as reference currency for prices in commodities (such as oil), as well as a larger component of foreign reserves by banks, has increased dramatically. Transactions in the currencies of commodity-producing countries, such as AUD, NZD, CAD, have also increased.